About AI in CleverStaff and beyond: what should a recruiter know?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming an increasingly popular assistant in recruitment, and especially in performing standardised tasks. For example, when it comes to searching, initial screening of candidates’ CVs, evaluating them based on unified criteria – that is, where there are many routine and repetitive operations. However, to have a good understanding of where AI can help recruiters and where it cannot, it is necessary to understand the technological context.
For instance, before OpenAI’s ChatGPT appeared in 2022, AI in business and IT was implemented mainly in the form of Machine Learning, which works well with similar tasks that have a set of structured data as input and a fixed list of solution options. For example, Machine Learning algorithms can determine the gender and approximate age of a person from a photo, make a diagnosis based on analyses, read text on a picture, etc.
What about recruitment?
Many start-ups have decided that a similar neural network can select the best candidates in a similar way. To do this, you need to pass it a job description and a certain number of resumes, and then it will tell you which one is the best fit.
It is clear that these efforts were doomed from the start. After all, a recruiter can’t immediately select the best candidate after reading a CV. Because this text is incomplete and insufficient information for decision-making, which still needs to be checked for truthfulness and relevance. Therefore, no AI can solve these problems if there is not enough data. Moreover, recruiters need to communicate at the interview, look at the candidate, and feel him or her. Therefore, AI cannot do without the information and impressions that people receive during personal communication.
What’s in CleverStaff?
It is expected that with the emergence of new AI technologies, such as ChatGPT, Google’s Gemini, and Meta’s Llama, many new classes of tasks have emerged that can be solved by AI implementations related to processing a text query and issuing a text response. This makes it possible to solve a large number of applied tasks.
However, this technology has even more promise when it has access not only to general data on the Internet but also to corporate data, which is needed by AI to answer tasks in a particular company.
At CleverStaff, we have just such a situation, when intelligent processing of corporate data significantly enhances the recruiter’s capabilities.
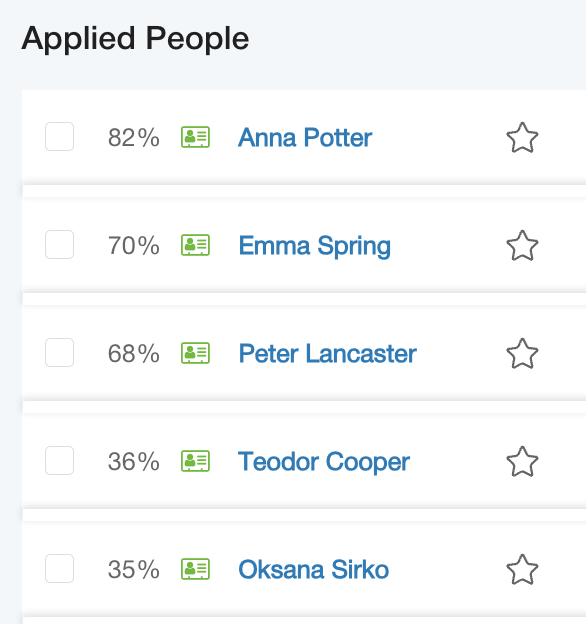
After all, we have current vacancies, a database of candidates, and candidates who have responded or have already been selected for a particular vacancy.
We ask AI to ‘read’ the job posting, ‘read’ the text of the candidates’ CVs or profiles, and rank them from most to least relevant. Of course, it does this in the context of the job requirements and the candidates’ eligibility.
It happens that sometimes there is not enough data for a more accurate ranking.
For example, the requirements include the desired number of years of experience, but the candidate’s profile does not. In this case, the AI suggests that the recruiter clarify it with the candidate. 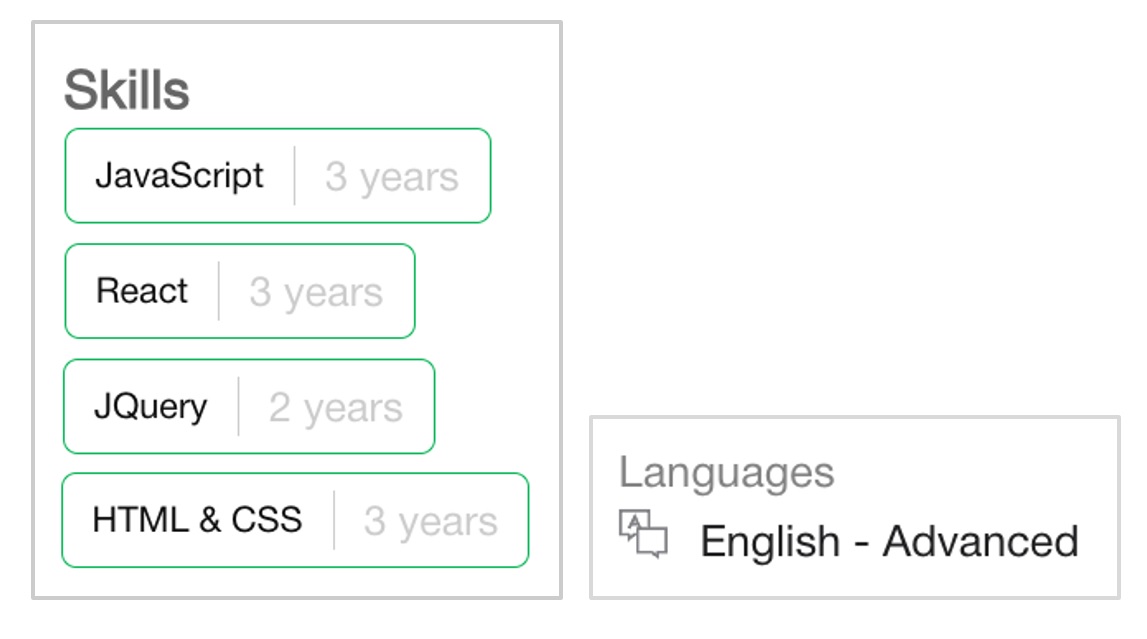
In turn, once the information is added to the database, the candidate ranking becomes even more accurate.
This allows the recruiter to prepare for the interview better and faster, and reduces the total number of interviews required.
As a result, the number of hires has increased by 13.6% (!), according to the results of our A/B test we recently completed.